Ce contenu n’est pas encore disponible dans votre langue.
Clustering
Clustering in ALTCHA Sentinel allows you to deploy multiple instances that share data across nodes, enabling high availability for mission-critical applications.
This guide applies to Sentinel version 1.9 and later.
Core Principles
- All nodes connect directly to PostgreSQL and Redis instances. Deploying a highly available setup for the databases is strongly recommended.
- Sentinel instances are stateless and do not require persistent storage, although persistence is recommended for efficient caching of external data sources such as threat intelligence data.
- Kubernetes is the recommended environment for multi-instance deployments.
Requirements
- PostgreSQL 15+ (required)
- Redis 7+ (required)
- ClickHouse 22.6+ (optional, supported only in the Enterprise plan)
Configuration
Enabling clustering is simple and requires only configuration of the PostgreSQL and Redis databases. The number of instances can be scaled up or down as needed. The number of instances is limited by the license.
Minimal ENV configuration example:
# LicenseLICENSE_KEY=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
# DatabasesPOSTGRES_URL=postgresql://user:password@localhost:5432/altcha_sentinelREDIS_URL=redis://default@localhost:6379
# Auto-generate secrets from the seed (CHANGE THE SEED VALUE)SECRET_SEED=3Wtd47Um6JxIYUO9Wz27g448Enabling PostgreSQL
Clustering requires an external PostgreSQL instance, which will be used as the primary database for Sentinel. To enable PostgreSQL, configure the POSTGRES_URL environment variable:
POSTGRES_URL=postgresql://user:password@localhost:5432/altcha_sentinelMake sure to use PostgreSQL version 15 or later (version 17 is recommended).
Migrations are handled automatically on application startup.
For details on configuring TLS/SSL connections and certificates, see the Performance Tuning documentation.
Enabling Redis
In addition to PostgreSQL, you’ll also need to configure a Redis instance, which is used to store shared state, such as rate-limiting data, and to provide pub-sub functionality for Sentinel instances.
REDIS_URL=redis://default@localhost:6379When using Redis Cluster, configure REDIS_CLUSTER_URL instead and point it to the Redis Cluster configuration endpoint.
For more details on using Redis Cluster or Redis Sentinel deployments, see the related ENV variables.
Make sure to use Redis version 7 or later, or another Redis-compatible database such as Valkey 7.
Enabling ClickHouse
The Enterprise plan allows integration with ClickHouse for analytics and logs, improving scalability and data availability. To enable it, configure the CLICKHOUSE_URL environment variable:
CLICKHOUSE_URL=http://user:password@localhost:8123/altcha_sentinelMake sure to create the database and tables as described in the ClickHouse documentation.
Other ENV Variables
NODE_ID
Each instance must have a unique NODE_ID. This value is randomly generated on startup (and persisted on the data volume), but you can configure your own NODE_ID. The value can be any short string, such as node_1.
SECRET_SEED
Sentinel requires several cryptographic secrets to be configured. You can set them directly as described in the ENV Variables documentation, or you can use SECRET_SEED to cryptographically generate all required secrets from a fixed seed value. Using SECRET_SEED allows you to easily configure secrets that are shared across all instances. Set this to a randomly generated secret seed of sufficient length (24 characters recommended).
Database Unavailability
ALTCHA Sentinel handles database unavailability gracefully, ensuring continuous operation with limited capabilities and minimal disruption.
PostgreSQL
Data required for basic Sentinel operations — such as API keys and Security Group configurations — is loaded into memory on application startup and synced whenever changes occur. This allows Sentinel to remain partially operational even if PostgreSQL becomes unavailable, ensuring that critical endpoints for ALTCHA verification and classification continue to function. However, features that require an active database connection — such as Forms, Redirects, and Training data — will not be available. Any attempts to modify data will fail if the database is unreachable.
Redis
Redis is used to store shared state, such as rate-limiting data. When Redis becomes unavailable, Sentinel automatically falls back to in-memory rate-limiting and attempts to reconnect periodically. This mechanism ensures continued operation even during Redis outages. However, features that rely on Redis pub-sub require an active connection (such as cluster node discovery, in-memory data sync) and will be unavailable until Redis is accessible again.
ClickHouse
When configured, ClickHouse is used to store request logs. If ClickHouse becomes unreachable or data cannot be written, request logs will be lost. This does not affect core functionality, but historical analytics data will be incomplete for the affected period.
Multi-Regional Deployments
Deploying ALTCHA Sentinel in multiple regions is the most effective way to reduce latency and improve performance for users around the world.
A multi-regional setup consists of multiple Sentinel instances or clusters deployed in different geographical regions. Each regional deployment runs its own Redis instance while sharing the same Postgres database across all regions.
This approach ensures:
- Low latency for users by serving requests from the nearest region.
- Consistent configuration through a shared Postgres database.
- Simplified infrastructure without the complexity of cross-region replication.
Redis is used to store the cluster state, including used tokens that prevent replay attacks. Each region operates its own local Redis instance, which does not need to be replicated, since each region serves a distinct group of geographically separated users.
Optionally, to make cross-region token reuse impossible, you can configure a unique ALTCHA_HMAC_SECRET for each region, ensuring that challenges generated in one region cannot be used in another.
Postgres stores configuration data such as API keys, security groups, and account settings. These values are cached in memory by Sentinel, which means a single shared Postgres cluster is sufficient even for global deployments, as database queries are infrequent. To further reduce database load, adjust the environment variables for caching.
For distributed deployments, use ClickHouse for efficient cross-region analytics. Alternatively, you can disable request logging in the API key configuration to minimize load on Postgres.
Because Redis is not replicated between regions, some internal features will not synchronize between regions:
- Cluster-wide pub/sub communication and instance discovery
- In-memory cache purges (must be triggered separately in each region)
These limitations only affect internal runtime behavior and do not impact normal API operations or verification functionality.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is the recommended platform for deploying a cluster. For details on getting started, see the Kubernetes guide.
To deploy a cluster using Kubernetes, create a secret containing your connection strings and secret seed:
kubectl create secret generic altcha-sentinel-secrets \ --from-literal=LICENSE_KEY=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX \ --from-literal=POSTGRES_URL=postgresql://... \ --from-literal=REDIS_URL=redis://... \ --from-literal=SECRET_SEED=...Add the configuration to your values.yaml file:
# Set the number of pods to runreplicaCount: 3
# (Optional) Disable persistent volumes.# Keep persistence enabled for efficient caching of external data sources such as threat intelligence data.persistence: enabled: false
# Load ENV variables from the secretenvFrom: - secretRef: name: altcha-sentinel-secretsThen install the HELM chart using your values.yaml:
helm install altcha-sentinel altcha-org/sentinel -f values.yamlAutoscaling and Persistence
Autoscaling is disabled by default. If you enable it, it is recommended to disable persistence, as new Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs) will be created for each replica.
Dashboard
The dashboard shows all instances in the cluster. Each instance displays the last 60 minutes of basic server metrics, such as CPU and memory usage.
The cluster dashboard is visible only to users with root privilege.
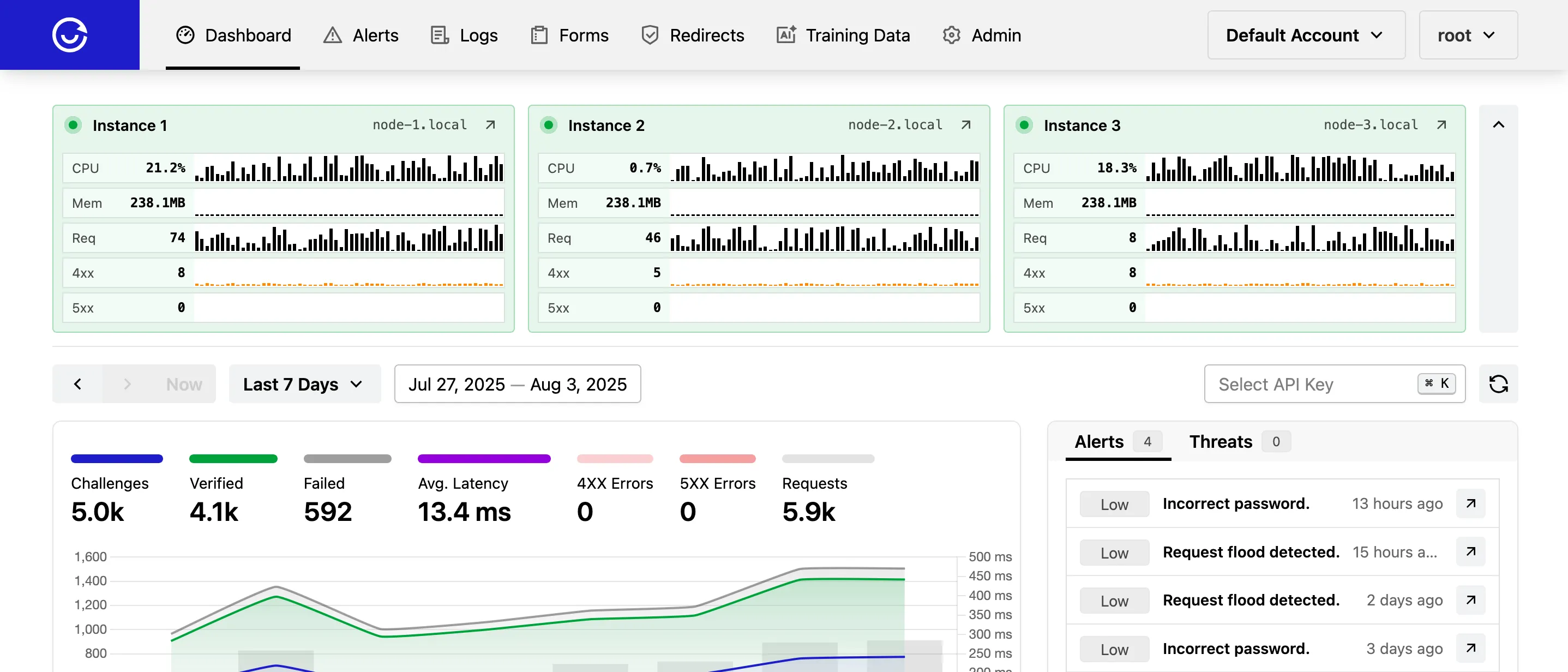
Basic Instance Metrics
CPU– Average CPU usage in percent.Mem– Average memory usage (RSS).Req– Number of requests per minute.4xx– Number of 4xx HTTP errors per minute.5xx– Number of 5xx HTTP errors per minute.
For detailed metrics, see Monitoring and Logging.
Limitations
- ENV variables cannot be set from within the application. The License Key must be configured via the
LICENSE_KEYenvironment variable. - Snapshots are not enabled when PostgreSQL is used. For database backups, use standard backup solutions for PostgreSQL.
Number of Replicas
Do not configure more replicas than your license allows. The license server provides a grace period to accommodate pod rescheduling, but if you exceed the licensed limit, it will eventually shut down the oldest instances.